10 조건문
else
if만으로는 좀 더 복잡한 상황을 처리하는데 부족하다. 아래의 그림처럼 if-else절은 if 절의 값이 true일 때 then절이 실행되고, false일 때 else절이 실행된다.
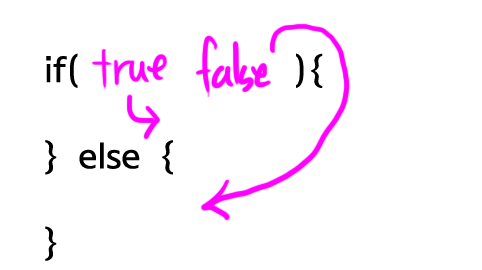
아래 예제를 보자. 결과는 1이다.
package org.opentutorials.javatutorials.condition; public class Condition3Demo { public static void main(String[] args) { if (true) { System.out.println(1); } else { System.out.println(2); } } }
다음 예제의 결과는 2다.
if(false){ System.out.println(1); } else { System.out.println(2); }
else if
else if절을 이용하면 조건문의 흐름을 좀 더 자유롭게 제어할 수 있다. if절의 값이 true라면 then절이 실행된다. false라면 else if절로 제어가 넘어간다. else if절의 값이 true라면 else if then절이 실행된다. false라면 else 절이 실행된다. else if절은 여러 개가 복수로 등장할 수 있고, else절은 생략이 가능하다. else 절이 else if 절보다 먼저 등장할 수는 없다.
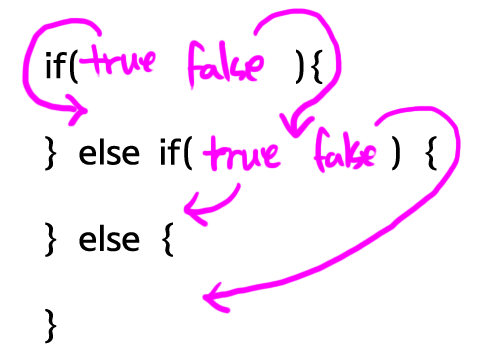
아래 예제를 보자. 결과는 2다.
package org.opentutorials.javatutorials.condition; public class ElseDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { if (false) { System.out.println(1); } else if (true) { System.out.println(2); } else if (true) { System.out.println(3); } else { System.out.println(4); } } }
다음 예제의 결과는 3이다.
if(false){ System.out.println(1); } else if(false) { System.out.println(2); } else if(true) { System.out.println(3); } else { System.out.println(4); }
다음 예제의 결과는 4다.
if(false){ System.out.println(1); } else if(false) { System.out.println(2); } else if(false) { System.out.println(3); } else { System.out.println(4); }
